7) Streams, rivers, and channels
## Lab 7: Rating curves & Mixing and Dispersion in Rivers
Download the lab and data files to your computer. First you will need the lab worksheet [Mixing and Dilution Worksheet](/Fluid_Flows/modules/lab7/CEE348_Spring_2022_Week9Lab.pdf) This is will be part of Homework 8, but we want to start early.
* [Lab 7-1: Rating Curves](/Fluid_Flows/modules/lab7/lab7-1.ipynb)
* data: [Lyell_h_Q_sorted.mat](/Fluid_Flows/modules/data/Lyell_h_Q_sorted.mat)
* image: [LyellForkTuolumnegagesite](/Fluid_Flows/modules/lab7/LyellFork_Tuolumne_flowcontrol.png)
* Note, this python workbook is optional, if you are interested in how rating curves are made.
* [Lab 7-2: Mixing and Dispersion in Rivers](/Fluid_Flows/modules/lab7/lab7-2.ipynb)
* data (to examine not in python): [CEE348_dye_data_Lab7.xlsx](/Fluid_Flows/modules/data/CEE348_dye_data_Lab7.xlsx)
* data (to examine in python): [Dye_data_GA050630c.csv](/Fluid_Flows/modules/data/Dye_data_GA050630c.csv)
Homework 7:
Problem 1: (note, we solved this together in lab class, but you need to turn in your write-up for homework)
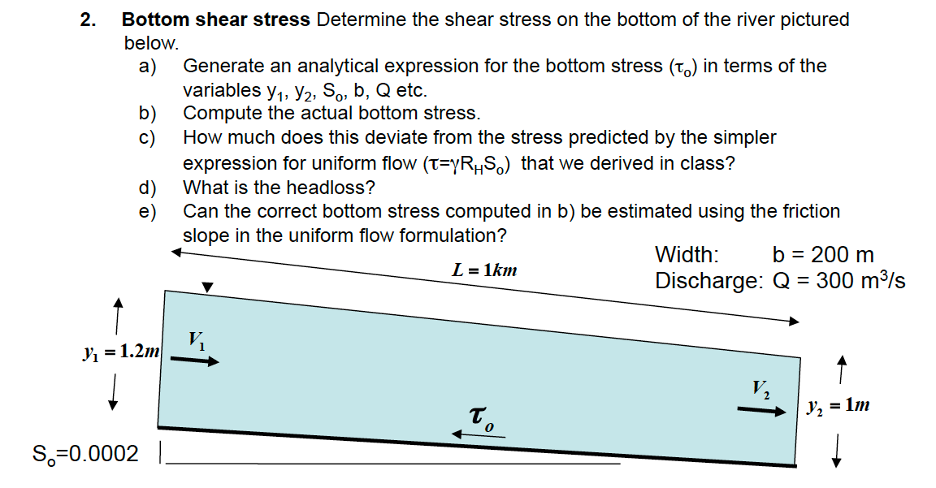 Hints: For 1a, use the full conservation of momentum expression derived in class, before we simplified using uniform flow. Remember that the friction slope, Sf = hL/L (head loss divided by the length). For 1b, use the expression you generated in 1a.
Hints: For 1a, use the full conservation of momentum expression derived in class, before we simplified using uniform flow. Remember that the friction slope, Sf = hL/L (head loss divided by the length). For 1b, use the expression you generated in 1a.
- Friction slope
- a) Using the values from Problem 1, above, justify why it is common practice to use the water surface slope (Ssurface) as an approximation for the friction slope (Sf). (Hint: Use your equation from above with both values plugged in and see how different they are.)
-
b) What is the percent difference between the actual friction slope and the water surface slope?
-
c) When would you expect the difference between Ssurface and Sf to be large?
Probelm 2: River bed erosion
To avoid erosion, the river bed is armored with large cobbles, increasing the bed resistance. In a 1km section of the river the depth decreases from 1.9 m to 1.5 m. For this calculation you are told that the discharge is 44 m3/s. The channel bed slope and width can be considered to be the same as in the prior problem. Determine:
- The head loss and friction slope
- The shear velocity, u*